
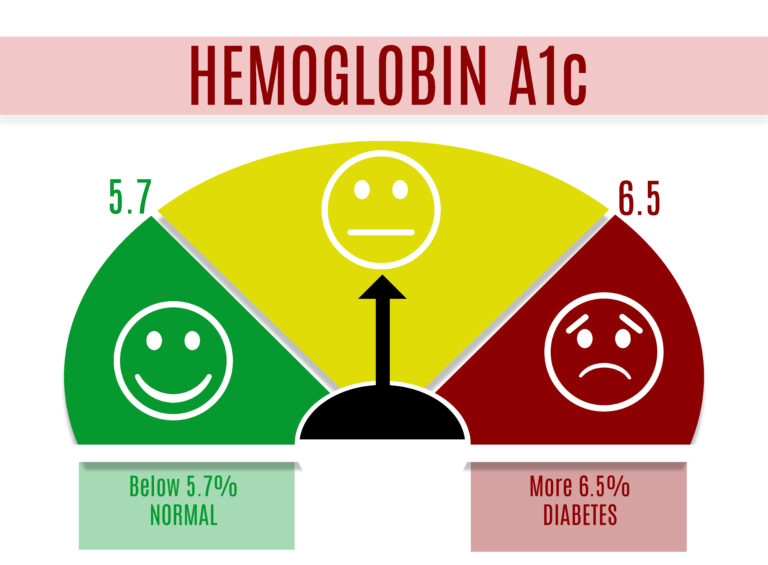
Hemoglobin A1C Test is the measure of a person’s average blood glucose level over the past 2 to 3 months. Hemoglobin is the part of a red blood cell that carries oxygen to the cells and sometimes joins with the glucose in the bloodstream. The test shows the amount of glucose that sticks to the red blood cell, which is proportional to the amount of glucose in the blood. Results are given as a percentage or as an average glucose value.
A procedure to cut off a limb, such as a foot, from the body.
A cell located in the pancreas that makes insulin.
A type of fat produced by the liver and found in the blood. Cholesterol is also found in some foods. The body uses cholesterol to make hormones and build cell walls.
The main sugar found in the blood and the body’s main source of energy.
The force of blood exerted on the inside walls of blood vessels. Blood pressure is expressed as two numbers with units of millimeters of mercury (mmHg). For example, a blood pressure result of 120/80 mmHg is said as “120 over 80.” The first number is the systolic pressure, or the pressure when the heart pushes blood into the arteries. The second number is the diastolic pressure, or the pressure when the heart rests.
A measure used to evaluate body weight relative to a person’s height. BMI is used to find out if a person is underweight, normal weight, overweight, or obese.
Disease of the heart and blood vessels (arteries, capillaries, and veins).
Any condition that causes reduced kidney function over a period of time. CKD is present when a patient’s glomerular filtration rate remains below 60 milliliters per minute for more than 3 months. CKD may develop over many years and lead to end-stage renal disease. Also see End-Stage Renal Disease.
Heart disease caused by narrowing of the arteries that supply blood to the heart. If the blood supply is cut off the result is a heart attack.
A condition characterized by hyperglycemia (high blood glucose) resulting from the body’s inability to use blood glucose for energy. Also see Type 1 Diabetes and Type 2 Diabetes.
An emergency condition in which extremely high blood glucose levels, along with a severe lack of insulin, result in the breakdown of body fat for energy and an accumulation of ketones in the blood and urine. Signs of DKA are nausea and vomiting, stomach pain, fruity breath odor, and rapid breathing. Untreated DKA can lead to coma and death.
Causes vision damage to the small blood vessels in the retina. Loss of vision may result, and is also called diabetic eye disease.
The process of cleaning wastes from the blood artificially. This job is normally done by the kidneys. If the kidneys fail, the blood must be cleaned artificially with special equipment. The two major forms of dialysis are hemodialysis (using a machine to clean wastes from the blood after the kidneys have failed) and peritoneal dialysis (using the lining of the abdominal cavity, or belly, as a filter to clean the blood).
Total and permanent kidney failure. When the kidneys fail, the body retains fluid. Harmful wastes build up. A person with ESRD needs treatment to replace the work of the failed kidneys.
Also called impotence, is the inability to get or maintain an erection for satisfactory sexual intercourse.
A type of diabetes that only develops during pregnancy and usually disappears after delivery. It increases the mother’s risk of developing diabetes later in life. GDM is managed with meal planning, physical activity, and, in some cases, medication.
Measure of kidney function, the rate at which the kidneys filter wastes and extra fluid from the blood, measured in milliliters per minute.
A fat found in the blood that takes extra cholesterol from the blood to the liver for removal, sometimes called “good” cholesterol. Also see Blood Cholesterol.
An emergency condition in which one’s blood glucose level is very high and ketones are not present in the blood or urine. If not treated, it can lead to coma or death.
Also called high blood pressure, a condition present when blood flows through the blood vessels with a force greater than normal. Hypertension can increase the risk of heart attack, stroke, kidney problems, and death.
Also called low blood glucose, a condition that occurs when one’s blood glucose is lower than normal, usually below 70 mg/dL. Signs include hunger, nervousness, shakiness, perspiration, dizziness or light-headedness, sleepiness, and confusion. If left untreated, hypoglycemia may lead to unconsciousness.
A condition in which a fasting blood glucose test shows a level of glucose higher than normal, but not high enough for a diagnosis of diabetes. IFG, also called prediabetes, is a level of 100 to 125 mg/dL. People with prediabetes are at increased risk for developing type 2 diabetes, heart disease, and stroke.
A condition in which blood glucose levels are higher than normal, but are not high enough for a diagnosis of diabetes. IGT, also called prediabetes, is a level of 140 to 199 mg/dL 2 hours after the start of an oral glucose tolerance test. People with prediabetes are at increased risk for developing type 2 diabetes, heart disease, and stroke.
A hormone that helps the body use glucose for energy. The beta cells of the pancreas make insulin. When the body cannot make enough insulin, insulin is taken by injection or other means.
This insulin-delivering device is about the size of a deck of cards and can be worn on a belt or kept in a pocket. An insulin pump connects to narrow, flexible plastic tubing that ends with a needle inserted just under the skin. Users set the pump to give a steady trickle or basal amount of insulin continuously throughout the day. Pumps release bolus doses of insulin at meals and at times when blood glucose is too high, based on doses set by the user.
The body’s inability to respond to and use the insulin it produces. Insulin resistance may be linked to obesity, hypertension, and high levels of fat in the blood.
A type of diabetes, usually first diagnosed after age 30, in which people show signs of both type 1 diabetes and type 2 diabetes. Most people with LADA still produce their own insulin when first diagnosed and do not require insulin injections. Some experts believe that LADA is a slowly developing kind of type 1 diabetes because patients have antibodies against the insulin-producing beta cells in the pancreas. Several years after diagnosis, people with LADA must take insulin to control blood glucose levels.
A fat found in the blood that takes cholesterol around the body to where it is needed for cell repair and also deposits it on the inside of artery walls; sometimes is called “bad” cholesterol. Also see Blood Cholesterol.
Disease of the large blood vessels such as atherosclerosis, coronary heart disease, stroke, and peripheral vascular disease.
Swelling in the macula, the part of the retina in the eye, used for reading and seeing fine detail.
A monogenic (i.e., related to a single gene) form of diabetes that usually first occurs during adolescence or early adulthood.
Disease of the smallest blood vessels, such as those found in the eyes, nerves, and kidneys.
Disease of the kidneys causing damage that allows protein to leak out of the kidneys into the urine. Damaged kidneys can no longer remove wastes and extra fluid from the bloodstream.
Disease of the nervous system that causes muscle weakness, pain, and numbness. The most common form of neuropathy in people with diabetes is peripheral neuropathy, which affects the legs and feet.
Fat in the liver which can lead to nonalcoholic steatohepatitis—a common liver disease that occurs in people who drink little or no alcohol—and chronic liver disease. NAFLD can be a complication of insulin resistance and diabetes.
A procedure to remove through surgery damaged feet or legs, where the injury was not caused by trauma (e.g., the injury was not caused by a car accident).
A condition in which a greater than normal amount of fat is in the body; more severe than overweight; having a body mass index of 30 or more. See Body Mass Index.
Disease of the gums in the mouth.
A condition in which the large blood vessels of the legs are narrowed or blocked by fatty deposits, decreasing blood flow to the legs and feet. Also called peripheral vascular disease, PAD is marked chiefly by cramping pain, weakness, numbness, and tingling in the legs and it increases the chances of amputation, heart attack, and stroke.
A condition classified in people who have blood glucose or hemoglobin A1C levels higher than normal but not high enough to be classified as diabetes. People with prediabetes have an increased risk of developing type 2 diabetes, heart disease, and stroke.
A condition characterized by high blood glucose levels caused by a total lack of insulin. This occurs when the body’s immune system attacks the insulin-producing beta cells in the pancreas and destroys them. The pancreas then produces little or no insulin. Type 1 diabetes develops most often in young people but can appear in adults.